Why Does Cushing's Syndrome Occur? An Informative Look
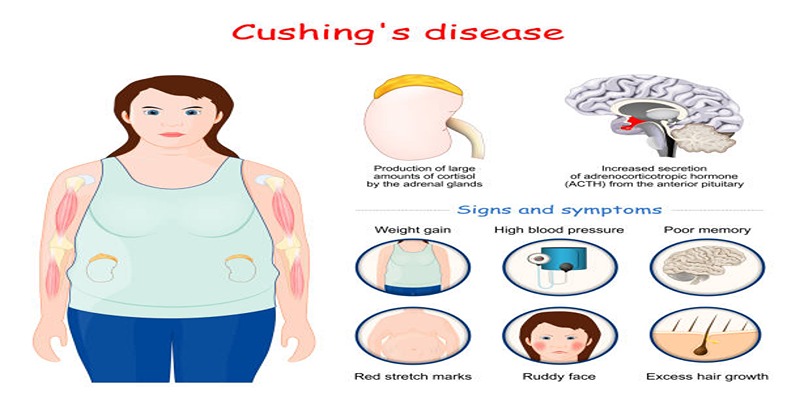
Cushing's syndrome is a condition that happens when there is too much cortisol, a hormone, in the body. Cortisol is important for controlling stress, blood sugar, and more, but having too much can cause problems. This syndrome can develop from various causes, like taking certain medications or changes in the body’s glands. People with Cushing's syndrome might notice unusual weight gain, skin changes, or feel tired. Understanding its causes and effects helps in early diagnosis and treatment, making it easier to manage and improve health.
Causes of Cushing's Syndrome
There are three main causes of Cushing's syndrome: excessive use of corticosteroid medications, a tumor in the pituitary gland, and a tumor in the adrenal glands. Let's take a closer look at each cause.
Corticosteroid Medications
Corticosteroids are widely used by physicians for treating different diseases including autoimmune, respiratory, and allergic states. These medications mimic one or more activity of cortisol in the body and may cause an increase in the level of cortisol when taken for long or in high levels. This results in overexposure to cortisol which leads to condition known as Cushing’s syndrome.
This can be avoided by adhering strictly to your doctor’s instructions particularly when you are using corticosteroids. You should never discontinue the medications, or decrease your doses without discussing it with your doctor first. They may assist you with keeping tabs on cortisol ratings and minimize any dangers in vogue.
Tumors in the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland, a small, bean-shaped organ situated at the base of the brain, plays a crucial role in hormone production. Among the hormones it releases is adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which prompts the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. However, in some cases, a non-cancerous tumor may form on the pituitary gland, leading to excessive ACTH production and elevated cortisol levels in the body.
If you have a pituitary tumor, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove it or prescribe medication to stop its growth. In some cases, radiation therapy may also be necessary.
Tumors in the Adrenal Glands
The body houses two adrenal glands, each perched atop a kidney, which play a vital role in producing cortisol. In rare instances, a tumor may form in one or both glands, leading to an overproduction of cortisol.
Surgery is the most common treatment for adrenal tumors. Your doctor may also prescribe medications to help manage your symptoms before or after the surgery.
It's important to note that not all tumors in the pituitary or adrenal glands will cause Cushing's syndrome. Some tumors may be benign and not produce any hormones, while others may cause different hormone imbalances. It's essential to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Other Possible Causes
In addition to the three main causes mentioned above, there are other factors that can contribute to Cushing's syndrome. These include:
- Inherited conditions: Some rare genetic disorders, such as McCune-Albright syndrome and Carney complex, can cause the development of tumors in the pituitary or adrenal glands.
- Lung cancer: Certain types of lung cancers can produce ACTH, leading to an increase in cortisol levels in the body.
- Obesity: People with obesity have a higher risk of developing Cushing's syndrome due to increased levels of fat tissue, which can produce cortisol.
If you have any of these risk factors, it's essential to be aware of the symptoms of Cushing's syndrome. Early detection and management can help prevent long-term complications associated with this condition.
Common symptoms of Cushing's Syndrome

Cushing's syndrome can cause a wide range of symptoms, which can vary from person to person. Some of the most common ones include:
- Weight gain: Excessive cortisol levels can cause weight gain, especially in the upper body, face, and neck.
- Skin changes: People with Cushing's syndrome may experience thinning and fragile skin that bruises easily. They may also develop stretch marks on their abdomen, arms, and breasts.
- Changes in menstrual cycle: Women with this condition may have irregular periods or stop menstruating altogether.
- Muscle weakness: Elevated cortisol levels can lead to muscle wasting and weakness.
- Mood changes: Cushing's syndrome can cause irritability, anxiety, and depression.
- High blood pressure: Excessive cortisol can increase blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
If you experience any of these symptoms or notice any other unusual changes in your body, consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How Cushing's Syndrome is Diagnosed
Diagnosing Cushing's syndrome can be challenging, as its symptoms are similar to other medical conditions. However, your doctor may conduct a series of tests to determine the underlying cause and rule out other possible diagnoses. These tests may include:
- Blood and urine tests: These tests measure cortisol levels in your body to determine if they are within normal range.
- Dexamethasone suppression test: This test involves taking a synthetic form of cortisol (dexamethasone) orally and monitoring cortisol levels in the blood and urine over 24 hours.
- Imaging scans: MRI or CT scans can help detect any abnormalities in the pituitary or adrenal glands that could be causing Cushing's syndrome.
- Petrosal sinus sampling: This test involves taking blood samples from veins in your petrous sinus (located near the pituitary gland) to measure ACTH levels and determine if a pituitary tumor is present.
Conclusion
Cushing's syndrome is a complex condition that can have various causes, including tumors in the pituitary or adrenal glands and long-term use of corticosteroid medications. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and osteoporosis. Early detection and proper management are crucial to prevent these long-term effects. If you experience any symptoms or have risk factors for Cushing's syndrome, speak with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.